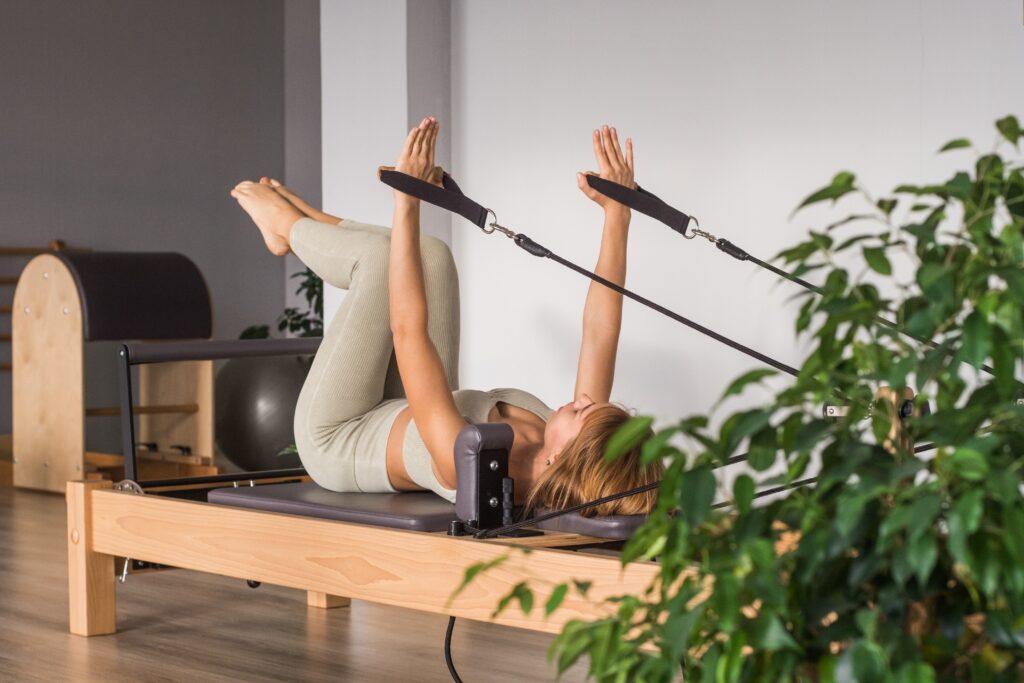

Pain free quality living with Pilates
spinal rehabilitation Training
Goal: Stop Progression of Spinal Curvature
01
Proper Breathing to Lengthen Muscles
Proper breathing is vital for scoliosis clients, and we not only will teach you proper breathing techniques, but we also will teach you to direct breathing into the concave side of the body to assist in lengthening atrophied muscles .
02
Restoration of Spinal Muscular Symmetry
We will strengthen the convex side of your curvature and lengthen the concave side to restore your muscular symmetry.
03
Realignment of Posture
We will strengthen your pelvic, hips, glutes, and abdominal stabilizer muscles to realign your posture and position you for success in maintaining alignment.
Success
By tailoring safe exercises to address the unique conditions of your body, Pilates assists in strengthening your spine\core, restoring your muscular symmetry, realigning your posture, and developing proper breathing techniques. Most clients experience noticeable improvement in only 3-6 months.

Special Populations
Conditions Treated
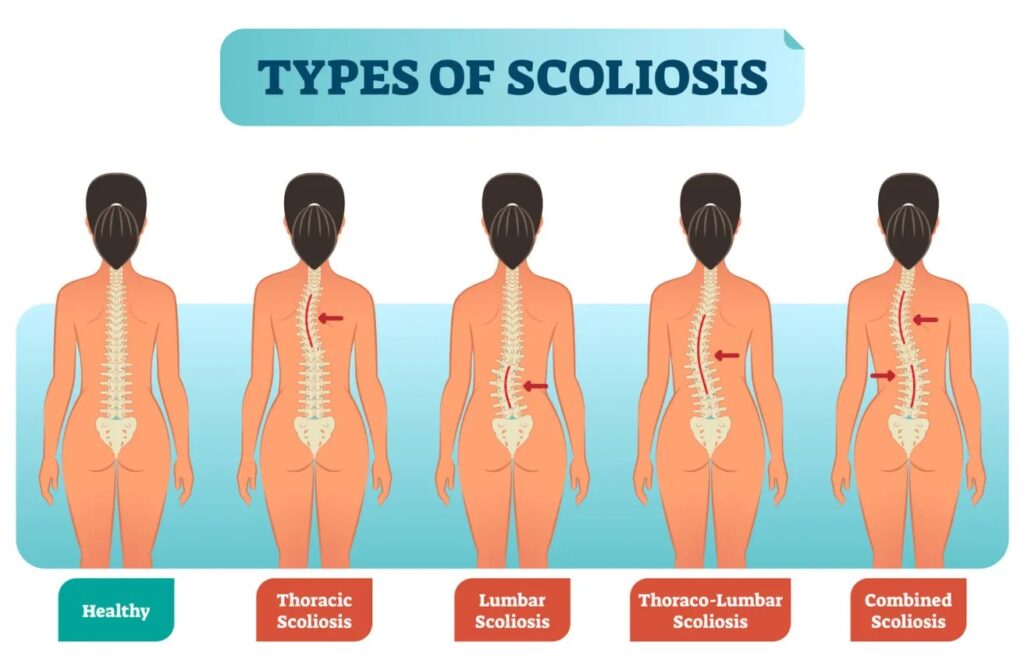
Scoliosis
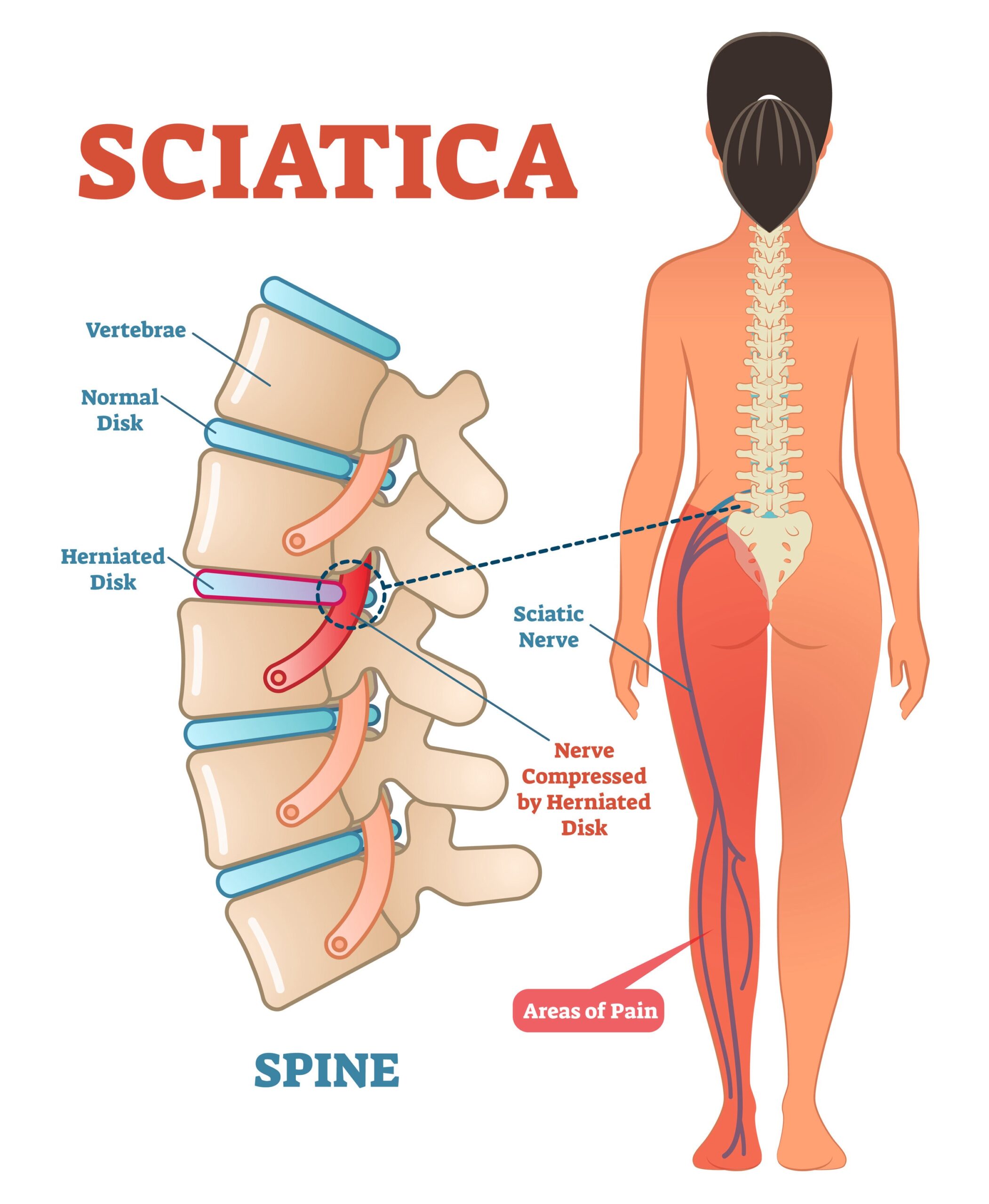
Sciatica

Spinal Stenosis
Have Questions?
Frequently Asked
Questions
What is scoliosis?
Scoliosis is a chronic, progressive disorder that causes the spine to curve (left: levoscoliosis/ right: dextroscoliosis) in either a single curvature (“C” curve) or a double curvature (“S” curve). The body compensates to these curvatures by developing a convex side (lengthened, weak muscles) and a concave side (shortened, tight muscles).
What are the symptoms of Scoliosis?
Symptoms of scoliosis: differing shoulder height; differing shoulder blade position; prominence or asymmetry in ribs; differing heights of left/right back when bending forward; differing hip height; uneven arm length; and/or misalignment of head.
How is scoliosis diagnosed?
Scoliosis is most often diagnosed during physical examinations by observation of patients standing, bending, and walking. X-rays are taken to confirm observations and determine the percentage of curvature. A “Cobb Angle” greater than 10% curvature will result in a scoliosis diagnosis.
Are there different types of scoliosis?
The most common type of scoliosis (80%) is idiopathic (infantile 0-3, juvenile 4-10, adolescent 11-18, adult 18+), which is genetic. There is also congenital scoliosis, which is due to birth defect; neuromuscular scoliosis, which is due to neuromuscular defect (cerebral palsy, spina bifida, Marfan syndrome); and degenerative scoliosis, which is due to gradual degeneration of spinal discs, vertebrae, and facet joints and becomes common around age 40 and more prevalent at age 60.
What are the treatment options for scoliosis?
Until spinal curvature reaches 20% or greater, the primary treatment options are physical therapy and\or pain management (steroid medications, injections, and epidurals or narcotic pain medication). Aquatic therapy has become a popular treatment as has Pilates exercise. Once spinal curvature exceeds 20%, external orthotic spinal bracing is often prescribed and curvatures that surpass 50% require internal spinal bracing (surgery).
What makes Pilates a safer program than other exercise programs?
Great question! Not only does Pilates focus on whole body health, it also focuses on the body’s powerhouse – the core (spine and abdominal muscles, which supports all other parts of the body and the mind-body connection (breathing and form). Pilates equipment is designed to assure proper form and to support the spine until strengthening has been regained. Tailored exercises to individual bodily conditions also support proper form through variations, modifications, progressions, and regressions. Most other programs are not as flexible (equipment or exercises) to accommodate unique bodily conditions.

We’re results-driven
so you can get back to enjoying life.
✓ Nationally Certified Instructors
✓ Personalized exercise programs
Testimonials
Our Customers Said




★ ★ ★ ★ ★
4.85 from 1,300+ reviews
“Amazing Results”
A must try for all who suffer with chronic spinal pain! I was skeptical, but the proof is in the results. This is the best exercise program I have experienced for scoliosis. My spinal curvature was gradually worsening and muscle spasms were increasing in frequency and size, but my last x-ray revealed a different story. My back feels great. Highly recommended!
★ ★ ★ ★ ★
— Michael DiPietro
“Knowledgeable Trainer”
The instructor did a thorough evaluation of my physical history, listened to my concerns, and helped me establish realistic goals (short and long term). I have finally found a program that is making a difference without compromising further injury. It has only been three months and the difference is already night and day. Pilates will be a part of my life for the rest of my life!
★ ★ ★ ★ ★
— Joy Johnston
“Outstanding Exercise Program”
The resistance equipment, safety techniques and mind-body connection form the best program I have tried since my auto accident (nearly 20 years ago). I’ve tried many exercise programs and all of them eventually led to injury and more pain. I honestly did not think I would be able to do the exercises, but the reformer supported my spine and the trainer guided me step by step. I have not felt this great in a very long time. Will definitely be a regular member. Do Pilates. Do Life!
★ ★ ★ ★ ★
— Joseph Walker
DaVel Walker, Pilates Trainer | 770-317-6623 | [email protected]
